Estimate Your Body Fat Percent

Use this calculator to quickly estimate your body fat. You can get a basic estimate by entering height, weight, age and gender. For more detailed results you can use a tape measurer or a body fat caliper to measure your body.
This calculator returns lean body mass (LBM), fat body mass (FBM), body fat percent and body classification. We also offer calculators to help people reach weight loss goals & measure calories burned during a workout.
Achieving Your Ideal Body Fat Percentage
Being passionate about food directly affects your nutrition and health. As a culinary enthusiast, you benefit by learning how to prepare all sorts of delicious meals. Somewhere along the way, taking control of your diet can also help you develop healthier food choices.
However, passion for food does not always translate to a healthy diet. It’s easy to get carried away when you have access to epicurean feasts. And as with everyone, if you don’t watch what you eat, it will eventually take its toll on your health.
This is why it’s important to keep track your weight, especially your body fat mass. To estimate your body fat percentage, use our calculator above.
In this guide, we’ll talk about the ideal body fat percentage for men and women, risks of low or excess fat mass, and different ways you can measure your body fat. Finally, we’ll discuss how to achieve the right fat percentage for improved health.
What is the Right Body Fat Percentage (BFP)?

A person’s ideal body fat percentage depends on several factors, including their gender, age, and height. Since men and women differ greatly in body composition, it immediately affects a person’s ideal BFP. Generally, men have more muscle mass, while women tend to have higher fat mass.[1] Women have higher body fat percentage than men to support the menstrual cycle, which is crucial for bearing children.[2]
Body composition is the amount of fat relative to fat-free mass.[3] Fat-free mass or lean tissue is composed of muscles, essential organs, and bones. While the right amount of fat is necessary for health, having excess fat can impede your organ function and overall fitness. Likewise, people with optimal body composition tend to be healthier, can move easily, and are less susceptible to illness.
According to Healthline, the American College of medicine published an ideal body fat percentage chart.[4] It factors in age and body composition differences between men and women. You will also notice that body fat mass naturally increases with age. See the table below.
| Age | Men Healthy Body Fat % | Women Healthy Body Fat % |
|---|---|---|
| 20 – 29 | 7 –17% | 16 – 24% |
| 30 – 39 | 12 – 21% | 17 – 25% |
| 40 – 49 | 14 –23% | 19 –28% |
| 50 – 59 | 16 –24% | 22 –31% |
| 60+ | 17 –25% | 22 –33% |
Need a more specific BFP chart? The American Council on Exercises (ACE) released a chart which classifies men and women’s fat percentage under different fitness categories.[5] Take a look below.
| Classification | Men Body Fat % | Women Body Fat % |
|---|---|---|
| Essential fat* | 2 – 5% | 10 – 13% |
| Athletes | 6 – 13% | 14 – 20% |
| Fitness | 14 – 17% | 21 – 24% |
| Average | 18 – 24% | 25 – 31% |
| Obese | 25% and up | 32% and up |
The chart above is based on the percentage of essentials fats. It indicates the ideal amount of essential fats necessary for a man or woman to maintain core functions, such as brain development, inflammation control, and blood-clotting. Though it does not include age range, it provides the ideal body fat percentage specifically for athletes, fit individuals, those who are average in physique, and individuals who are obese.
Why should I know my fat percentage? The weighing scale does not show how much fat mass your body has. It’s also not the best way to measure the state of your health.
Even with a thin physique or average weight, it’s possible to have a high fat percentage. This is usually caused by a sedentary lifestyle and an unhealthy diet. Estimating how much fat you have compared to your muscle mass is a good indicator of health and fitness. It reveals how lean you are, which may not be apparent at first glance.
On the other hand, there are many medical complications associated with very low body fat. According to the University of Pennsylvania Body Composition fact sheet, low body fat may impair cardiovascular function, cause reproductive health problems, gastrointestinal issues, as well as shrinkage of internal organs.[6] Fat also serves to insulate your organs and the rest of your body. This is why it’s good to bulk up before the winter season; fat helps keep you warm during cold weather.
In contrast to low fat mass, the World Health Organization (WHO) states that being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for many types of illness, including the following diseases:[7]
- Heart disease and stroke
- Diabetes
- Osteoarthritis – disease of the joints
- Cancer – prostate, liver, breast cancer, etc.
How Does Body Mass Index (BMI) Differ from BFP?
BMI is a measurement of weight over height. It only accounts for body mass, which means it does not include differences in body composition.[8] It does not factor in muscle mass, organs, or bone density.
In a BMI scale, a bodybuilder may register as overweight. But take note that muscle is denser than fat. If we measure a bodybuilder’s fat percentage, we’ll see how low his fat mass is compared to lean muscle mass. In this respect, BMI is not an accurate indicator of lean muscle mass or fitness. A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition notes that body fat percentage may be a better indicator for risk of weight-related illness in patients.[9]
Furthermore, the US Military uses fitness and body composition standards in employing soldiers that can adequately perform the physical demands of service.[10] With this principle in mind, the US Navy imposes maximum weight and height guidelines for applicants.[11]
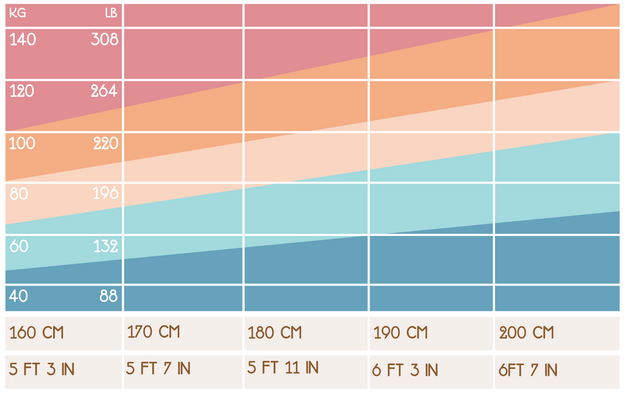
The following graphic shows how height and weight impacts BMI measurement.
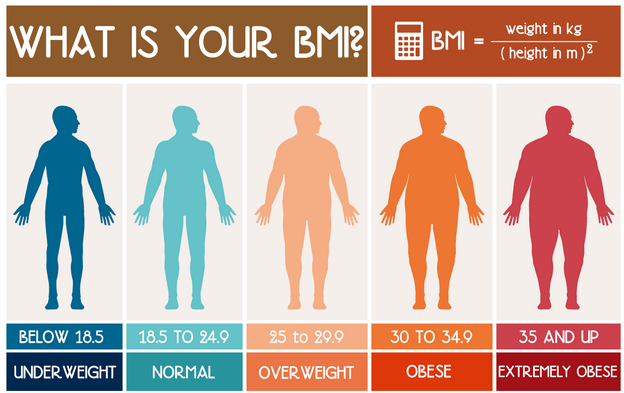
| BMI Score | Classification | US Pop | US Women | US Men |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight | |||
| 18.5 to 24.9 | Normal / Healthy Weight | |||
| 25 to 29.9 | Overweight | 32.5% | 26.5% | 38.7% |
| 30 to 34.9 | Obese | 30% | 30.5% | 29.5% |
| 35 and up | Extremely Obese | 7.7% | 9.9% | 5.5% |
The estimated prevalence of obesity statistics for US adults aged 20+ comes from the 2013-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).[12] Statistics in the above table are additive:
- 40.4% of United States adult women are either obese or extremely obese
- 70.2% of the United States population are either overweight or suffer from obesity
- 29.8% of the United States population are either underweight or a normal healthy weigh
BMI Formulas
- 703 x weight (lbs) / [height (in)]2
- weight (kg) / [height (m)]2
If height is shown in CM then divide it by 100 to convert it to meters. If height is shown in feet and inches multiply the feet by 12 and add that to the inches.
BMI Limitations
Again, BMI only measures body mass. A basic measure of BMI does not measure body composition. As mentioned above, some weight lifters may have a relatively high BMI. This is why it is important to use a tape measure or body caliper to obtain a more accurate reading which better reflects your true health.
Different Methods to Measure Body Fat

Estimating your body fat percentage is one way to track your health progress. This is especially helpful if you want to lose weight and gain lean muscles. You can start with a simple measuring tape and calipers, or even go to a healthcare center for more thorough measurements. The following are different ways to measure your body fat percentage.
1. Tape Measure Test
Using a tape measure is one of the most convenient ways to track BFP. This method is done by taking your height, weight, waist circumference, and neck measurements. In addition, hip circumference is taken for women.
A widely used body fat percentage equation was developed by the Naval Health Research Center (NHRC), with the following formulas below.[13]
- Men, Body Fat % = 495 / (1.0324 – 0.19077 * log10(waist – neck) + 0.15456 * log10(height)) – 450
- Women, Body Fat % = 495 / (1.29579 – 0.35004 * log10(waist + hip – neck) + 0.22100 * log10(height)) – 450
For a faster way to compute your body fat percentage, use our calculator on top of this page.
Because you need to take several measurements, the tape test has a lot of room for error. You must repeat measuring at least three times to ensure they are correct. Factors like your clothing, how tightly you pull the tape, and how recently you’ve eaten can affect the figures. It also pays to have a skilled person do the measurements to maintain precision.
2. Skinfold Caliper Test
Get your body fat percentage by performing a skinfold test. This is done with calipers that measure subcutaneous tissue (how thick your fat is) in different areas of your body. Calipers are also affordable and widely available tools to measure body fat. The popular 3-site approach was developed by researchers A.S. Jackson and M.L. Pollock.[14]
You can take the 3-site approach, a 4-site approach, or a 7-site approach to get your body fat percentage. These pinch tests can be done in the following skinfold sites:
- Abdomen – near the belly button
- Supraillac – the side of the tummy
- Triceps – fold behind arm
- Midaxillary – spot underneath armpit
- Subscapular – under the shoulder blade
- Chest – above nipple, toward the side
- Thigh – skinfold that’s around 4 in. above the knee
- For women – Area above the hip bone
For instance, a 4-site approach for men may include the abdomen, chest, tricep, and subscapular skinfold. For women, a 4-site approach may measure the area above the hip bone, abdomen, thigh, and the midaxillary area.
Just like the tape test, there’s plenty of room for error, especially if you’re not familiar with calipers. The skinfold test is said to have an error range of 3.5 – 5% body fat, according to Henry C. Lukaski, author of Body Composition: Health and Performance in Exercise and Sport.[15] Make sure to get an experienced professional before a caliper skinfold tests.
3. Body Fat Scale
This special scales utilizes bioelectrical impedence analysis (BIA) technology. It basically allows electrical current to pass through your legs all the way up to your body. These scales operate on the principle that fat conducts less electric current compared to muscle and water content in the body. Thus, it registers higher body fat percentage when it indicates more resistance.
To come up with a body fat percentage, this scale incorporates its bioelectrical reading with information such as your weight, height, age, and gender. Body fat scales are available in the market for around $35 and $50, depending on the brand.
However, according to Healthline, this tool may not provide very accurate results compared to previous methods.[16] Factors such as when your last meal was, your last exercise, and hydration level may affect the results. Some body fat scales may also not work well for athletes, older individuals, and children. Make sure to read the manual before purchasing one.
4. Hydrostatic Weighing
Hydrodensitometry, also known as hydrostatic weighing, is one of the most accurate methods for measuring body fat percentage. Steven Heymsfield, editor of the book Human Body Composition, states that hydrostatic weighing can have an error rate as low as 2% body fat.[17]
It’s more precise than traditional methods such as the tape test, skinfold test, or even the body fat scale. Due to its precision, it’s the ideal method for measuring body fat in both adults and children.
This method involves submerging individuals under water, and later on allowing them to exhale as much oxygen as they can from their lungs. The subject is then weighed back on land, while estimating how much air is still in their lungs. The result is calculated with a special formula that accounts for the body’s density. This number is then used to compute the subject’s body fat percentage.
While it’s one of the most accurate ways to measure fat mass, this procedure isn’t accessible for everyone. It can only be found in special facilities such as health clubs, universities, and large hospitals. Other limitations include subjects who are unable to completely go under water.
5. CT Scan and MRI
Another precise way to estimate body fat mass can be done through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computerized tomography (CT) scans. Apart from helping physicians look inside cross sections of your body, MRI and CT scans can help measure intra-abdominal fat.
Though this is not a common method, doctors have found a way to use these tools for their patients. A study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology used whole body MRI to quantify and evaluate different body fat deposits in 67 women.[18] The results showed that MRI results a great variation in total internal body fat which could not be predicted by measuring subcutaneous fat (skinfold) alone.
In a related study found in the Journal of Digital Imaging, researchers in Korea proposed to use CT scans for automated fat assessment.[19] The procedure was conducted on 5 male and 5 female participants. The results suggested that fat assessment using CT scans is reliable tool for estimating body fat.
While it’s one of the best methods out there, it comes with a major limitation. MRIs and CT scans cost a hefty sum. Depending on your facility, location, and insurance provider, CT scans and MRIs may cost somewhere around $300 up to a thousand dollars.
Reducing Body Fat with a Healthy Diet

Now we’ve come to the challenging part. Where do you start if you really want to lose excess fat? Weight loss is never easy, and can get overwhelming. Making huge diet changes may sound scary for anyone passionate about food. But if you start with little changes one step at a time, you can reach your ideal body fat percentage. And with your culinary skills, you can definitely whip up delicious and healthy meals.
Here are essential diet tips that can help you reduce body fat:
1. Cut the Carbs and Sugar – This means cutting back on dessert, including cake, doughnuts, and white bread. It’s also wise to stop buying processed snacks. Processed food is known to have high levels of sugar with glucose such as dextrin, dextrose, and corn syrup. Decreasing carbohydrates and sweets will help you lose the fat. How? According to the Mayo Clinic, the principle behind a low-carb diet brings about lower insulin levels. Lowered insulin helps the body burn stored fat for energy, which eventually leads to weight loss.[20] The less sugar and carbs you eat, the better.
2. Add More Fiber to Your Diet – Fiber is a carbohydrate in plant foods such as vegetables, greens, fruits, and whole grains. WebMD states that unlike regular carbs, it’s not easily broken down by your gut. In effect, it passes through your digestive tract without raising your blood sugar levels (insulin).[21] Examples of fiber-rich foods include kale, lentils, artichokes, raspberries and blueberries. While it doesn’t have fat-burning capabilities, eating more fiber aid weight loss by making you feel full longer. Adding more fiber into your diet allows you to eat more without actually consuming extra calories. Basically, eating fiber makes it easier to avoid snacks in between.
3. Eat Protein-Rich Foods – Consuming more protein also has satiating effects. Reaching for more protein instead of carbs helps reduce the hunger hormone ghrelin, while increasing appetite suppressing hormones such as GLP-1 and cholecystokinin.[22] Moreover, studies show that consuming a protein-rich diet helps you burn more calories. Protein has around 20-30% thermic effect compared to carbs with 5-10%.[23] The thermic effect of food is known as the increase in metabolic rate of ingestion. Examples of protein rich foods with high thermic effect include lean meat, salmon, eggs, and almonds. Finally, high protein foods helps you build lean muscles.
4. Do Intermittent Fasting – Fasting helps reduce your calorie intake since it helps you eat less. Studies have also shown that fasting for at least 48 hours helps increase metabolism by 3.6-14%.[24] There are different intermittent fasting methods, and a popular one for beginners is the 16/8 method. Under this fasting schedule, you skip breakfast daily and start eating only within an 8-hour feeding time. For instance, you skip breakfast and only eat meals between 12:00nn to 8:00pm. Other methods include two 24-hour fasts a week, and only eating 500-600 calories for two days in a week. Just remember to take baby steps; don’t do a 24 hour fast right away. It will likely be a very uncomfortable experience, discouraging you from fasting again. Start by skipping one meal before you fast with longer hours.
5. Try a Plant-based Diet – Some people can’t become vegetarians forever, but they can try cycling in and out of a plant-based diet for variation. Research published in Nutrients journal notes that plant-based diets can help reduce body fat with a variety of mechanisms such as reduced calories, improved gut bacteria, and increased insulin sensitivity.[25] These factors all together improve satiety as well as increased energy use which leads to weight loss. Apart from losing weight, a study in JAMA International Medicine notes that consuming plant-based protein can help you live a longer life.[26]
Exercises That Help Boost Muscle Mass

Aside from watching your diet, try to have a more active lifestyle. Simply moving more like taking longer walks or a quick run can help burn fat. But if you really want to build more muscle mass, doing strength training can help increase and maintain your muscles. Here are some exercises you can start doing to lose fat.
- Do Resistance Training – A workout that requires your muscles to exert resistive force is called resistance or strength training.[27] But apart from lifting weights and kettlebells, or pulling bands, there are other ways you can get resistance training. You can do body weight exercises such as pushups, pullups, and squats to help develop your muscles. Even without equipment, with just a couple of minutes a day, you can work those arms, hips, and glutes. Just be mindful of proper form for greater efficiency; also to avoid injury.
- Engage in Cardiovascular Exercises – While cardiovascular workouts or aerobic exercises don’t build muscle like weight training, it still helps with muscle growth. According to Men’s Health, aerobic exercises promote healing and repair of muscles after intense lifting workouts.[28] Examples of good aerobic exercises include dancing, running, jump ropes, jumping jacks and cycling. Any workout you perform with high intensity can fall under an aerobic exercise.
The Takeaway
Being a culinary enthusiast shouldn’t stop you from living a healthier lifestyle. In fact, your knowledge of different cuisines can really help you prepare nutritious and satisfying meals. Diet changes might seem overwhelming, but if you do them little by little, pretty soon you can develop healthier eating habits.
There are many ways to estimate your body fat percentage to track your progress. But if you want a convenient method, you can always use our calculator above for faster results. Keep in mind that beyond losing weight, you’re aiming for a strong and healthy body.
Want to know how much calories you can burn with your exercise routine? Use our workout calculator.
Sources:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11706283
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3117838
- https://med.virginia.edu/exercise-physiology-core-laboratory/fitness-assessment-for-community-members/body-composition/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-measure-body-fat#ranges
- https://www.acefitness.org/education-and-resources/lifestyle/tools-calculators/percent-body-fat-calculator/
- http://pennshape.upenn.edu/files/pennshape/Body-Composition-Fact-Sheet.pdf
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/features/body-fat-measurement#1
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10966886
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK221832/
- https://www.military.com/military-fitness/navy-fitness-requirements/navy-body-composition-assessment
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/overweight-obesity
- https://www.med.navy.mil/sites/nhrc/Pages/default.aspx
- http://www.umich.edu/~exphysio/mvs.240/AdditonalLabs/Pred.Bodyfat.Skinfold.6.3.pdf
- https://catalog.loc.gov/vwebv/search?searchCode=LCCN&searchArg=2016054140&searchType=1&permalink=y
- https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-measure-body-fat#ranges
- https://catalog.loc.gov/vwebv/search?searchCode=LCCN&searchArg=2004026523&searchType=1&permalink=y
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9804581
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3597966/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/low-carb-diet/art-20045831
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/features/fiber-weight-control#1
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16400055/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC524030/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2405717
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6893503/
- https://media.jamanetwork.com/news-item/eating-more-plant-protein-associated-with-lower-risk-of-death/
- https://www.menshealth.com/fitness/a19530279/resistance-training-to-build-muscle/
- https://www.menshealth.com/fitness/a19515630/long-runs-build-muscle/
